Use Variables in a Script
You must:
- Define variables
- Use them in action cells
Defining a User Variable
-
Expand the Variables panel by clicking its
 button.
button.
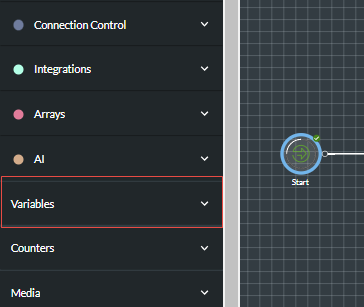
-
In the panel, use the Type field to select the type of variable you want to create and then provide a meaningful name in the Name field. The name must be unique in the script, begin with a letter, contain the characters a-z, A-Z, 0-9 or _ (underscore), and not contain spaces.
Note: you will not be able to edit the name of the variable once it has been created.
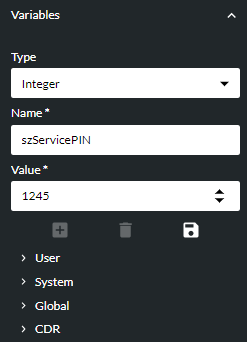
Tip: you can double-click a user variable type to start creating a variable of that type.
It is recommended that you include a prefix to help other users to identify the variable type at a glance. The following notation is often used by programmers:
|
Variable type |
Description |
Examples |
|
|
l |
Integer (lowercase l, not uppercase I) |
Stands for 'long integer' |
lCount |
|
sz |
String |
Stands for 'zero-terminated string' |
szServicePIN |
|
b |
Boolean |
Stands for 'Boolean' flag. |
bCaptured |
|
f |
Float |
Stands for 'floating point' variable. |
fBilledAmount |
|
dt |
Date |
Stands for 'date and time' |
dtCurrentDate |
|
arr |
Array |
Stands for 'array' An additional prefix can be used to indicate the type of data in the array. |
arrfPrices arrszCustInfo arrobjCustDetails |
|
obj |
Object |
Stands for 'object' |
objCust1Details |
|
tem |
Template |
Stands for 'email template' |
temStandard |
It is also recommended that, in variables containing multiple words, each word starts with an uppercase letter as this aids readability.
Constant variables (whose values are not expected to change within a service) are typically named in upper case. For example, 'lVAT_VALUE' and 'szDR_NUMBER'.
-
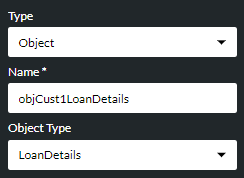
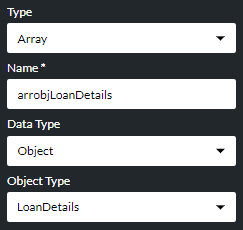
If you are creating a variable of type Object, use the Object Type options list to select the object type from the appropriate group (each object is listed under a group name that is based on the title of its associated OpenAPI specification).
Or, if you are creating a variable of type Array, use the Data Type options list to specify the type of data the array's elements will store.
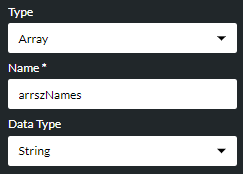
Note: if the array's data type is 'Object', you must choose that object's type from the Object Type options list:
-
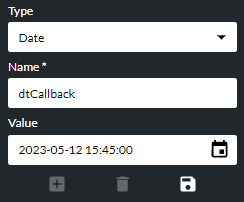
If the variable is required to have a starting (initial) value, enter this in the Variable Value field. For a date variable, the date and time must be entered in the format shown below. It is easier to click the
 button as this allows you to set the value graphically.
button as this allows you to set the value graphically.
-
Click the
 button to save the variable. The new variable is listed in the appropriate variable type section:
button to save the variable. The new variable is listed in the appropriate variable type section:

In languages that use Latin characters, variables are listed alphabetically (based on the ECMAScript standard). This does not apply to elements in structured variables such as date elements and object members.
Note: to edit a variable's starting value, select it, edit the value in the Variable Value field and then click the  button.
button.
- To add another variable, click the
 button (or double-click the variable type) and repeat the steps above.
button (or double-click the variable type) and repeat the steps above.
Note: you can also create a structured Call Data user variable to store system-generated call data (see the Call Data system variable) for use in an Outbound Call action cell.
Note: to delete a variable, select it and then click the  button.
button.
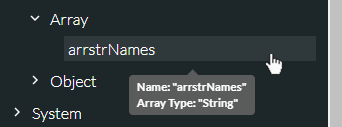
Hovering your mouse cursor over a variable in the Variables panel displays a tooltip indicating the variable's data type. This is particularly useful for array variables and for structured variables such as objects. The following illustration shows that the array variable arrstrNames is of type String.
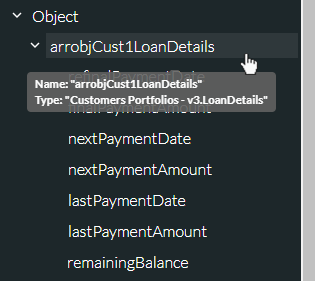
The tooltip for an object variable indicates the variable's object type and the group name separated by a dot. According to the following tooltip, the object variable arrobjCust1LoanDetails is of type 'LoanDetails' and is from the 'Customer Portfolios - v3' group.
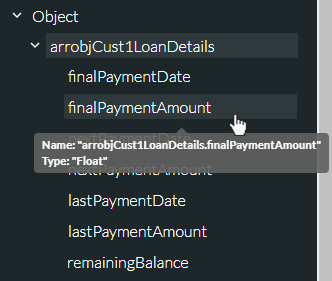
The tooltip for an object member indicates the member's data type. According to the following tooltip, the object member finalPaymentAmount is of data type Float.
Using a Variable in an Action Cell
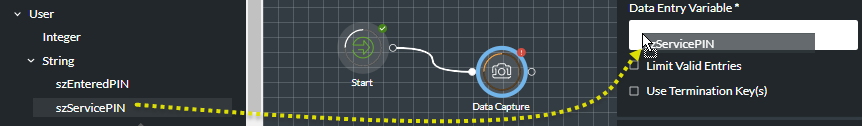
Either type the name of the variable in an action cell field that supports variables or drag it directly from the Variables panel and onto the target field.
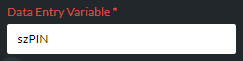
Note: a red parameter name indicates an undefined variable:
Some action cells accept only individual date-time elements rather than the entire date structure. To use a date variable in such a cell (for example, in the Fill Date action cell), expand the desired date variable in the Variables panel and then drag a date element to the target field in the action cell's properties:
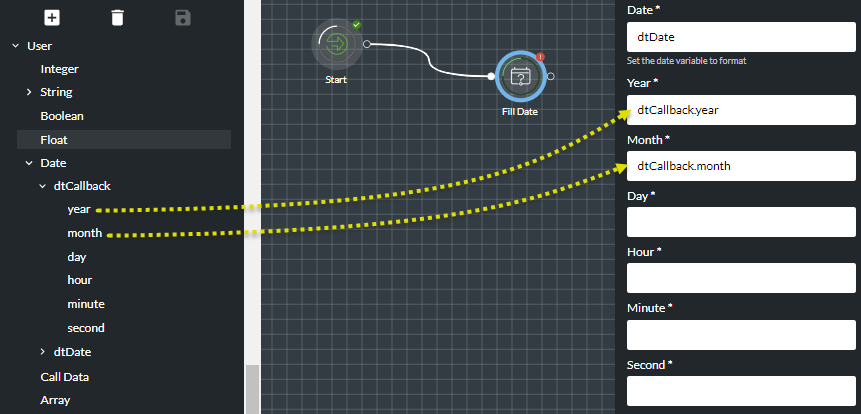
Note: leaving a date element empty causes the value to be converted to zero. This may be regarded as an invalid date format and may cause action cells such as Compare Variables to error.
If you are typing the name of a global variable in an action cell property, be sure to include the '$' symbol in the variable name.